Research
Research
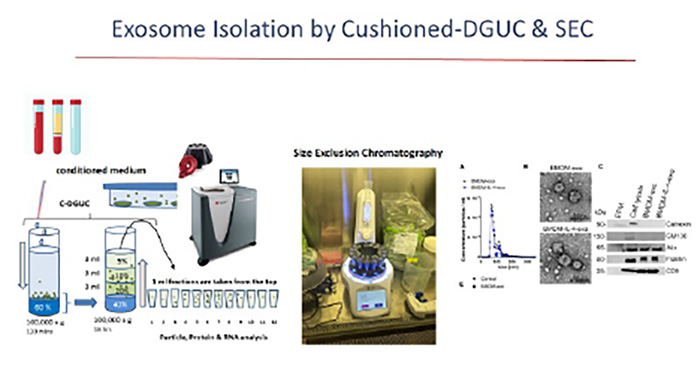
Macrophage Exosomes in Diabetic AtherosclerosisOur work revealed that hyperglycemia causes an enrichment of miR-486-5p in exosomes produced by cultured macrophages and those isolated from the plasma of human diabetic subjects suffering from cardiometabolic inflammation and atherosclerosis. Ongoing studies examine miR-486-5p as a source of atherosclerosis acceleration in diabetes. | |
Exosomes produced by IL4-Polarized Macrophages Control AtherosclerosisOur findings identified IL4-polarized macrophages (IL4-exo), commonly known as “M2-macrophages” as a source of anti-inflammatory exosomes. MicroRNA cargo present in IL4-exo were identified as a source of their protective signaling properties. The microRNA enriched in IL4-exo robustly increased mitochondrial respiration, oxidative phosphorylation and suppressed inflammatory signaling by communicating this cluster of microRNA to recipient cells that reprogrammed bioenergetic metabolism. | |
IL4-Macrophage Exosomes Control Cardiometabolic Inflammation & Diabetes in ObesityOur more recent findings revealed a capacity for IL4-exo to improve mitochondrial function in white adipose tissue that improved insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in obese diabetic mice. Our findings support the use of IL4-exosomes as novel therapeutics to control cardiometabolic diseases. | |
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) Isoforms & Macrophage Exosomes: Impact on Immunometabolism, Atherosclerosis and NeurodegenerationOur team has built on a rich legacy of ApoE-related research in lipoprotein metabolism, inflammation and atherosclerosis. Recently, our findings uncovered that ApoE serves as a natural immune checkpoint in atherosclerosis by restricting myeloid cell activation through an intrinsic capacity to modulate cellular microRNA levels |