Atherosclerosis Research Lab - Homepage

Extracellular Vesicles and Metabolic Regulation of Immunity in Atherosclerosis & Cardiometabolic Diseases
Atherosclerosis Research Lab

Extracellular Vesicles and Metabolic Regulation of Immunity in Atherosclerosis & Cardiometabolic Diseases
Atherosclerosis Research Lab
Research
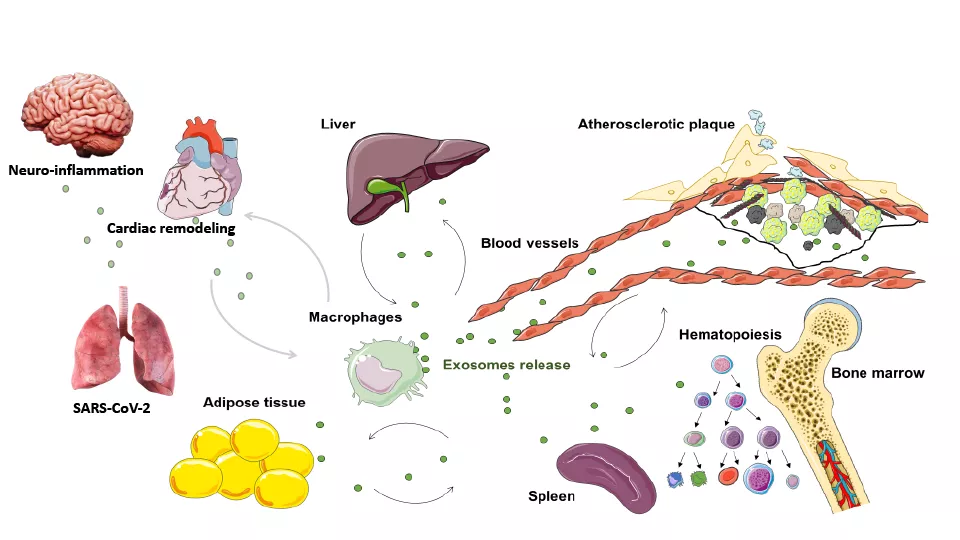
Our laboratory pioneered novel approaches to isolate Exosomes from conditioned cell culture media and biofluids for their subsequent study as biomarkers and contributors to cardiovascular inflammation and atherosclerosis.
Recent Publications
Featured News
Support the Lab
A gift to the Atherosclerosis Research Lab helps support research for atherosclerosis-related cardiovascular diseases.

Join Our Team
We have an open position for a Postdoctoral Fellow. Join our outstanding research team.


 PubMed
PubMed